Did you know that vitamin D deficiency symptoms are linked to over 20 health conditions? Learn about the symptoms and causes of Vitamin D deficiency, and how to prevent it.
Few foods from Trusted Source naturally contain vitamin D, and when they do, the amounts are frequently insufficient for a person to consume the necessary amount each day.
In response, producers added vitamins to a number of foods.
50% of people worldwide, according to a 2020 study by Trusted Source, do not consume enough vitamin D. In the US, 35% of adults suffer from the deficiency.
The risk of vitamin D insufficiency is higher in elderly folks, obese people, and those residing in healthcare institutions like hospitals.
What are Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms?
frequent diseases or infections
Vitamin D regulates the immunological function and suppresses inflammatory responses, which serves to maintain the immune system.
fatigue and weakened muscles
Lack of vitamin D deficiency symptoms can cause weakened bones and muscles, which can cause weariness because vitamin D is essential for maintaining healthy bones.
Bone and joint pain
Vitamin D can stop bone loss and boost trusted Source bone mass. An absence of vitamin D may be the cause of joint and bone discomfort.
Fractures
Enough vitamin D in the body supports calcium absorption, which maintains bone strength.
This is crucial for females after menopause, when bone density can decline and the risk of osteoporosis can rise, according to the National Osteoporosis Foundation.
Depending on the patient’s age and medical history, the doctor may check a patient’s vitamin D level if they have a fracture.
Depression
Lower vitamin D levels may raise the risk of depression, according to the authors of a 2019 analysis.
Research suggests that vitamin D has a beneficial anti-inflammatory impact, and there are vitamin D receptors in the brain.
The researchers draw the conclusion that a person with depression and very low vitamin D levels may benefit from taking a vitamin D supplement.
wounds heal slowly
Low vitamin D levels may cause wounds to heal more slowly than usual.
outcomes of an in vitro experiment
According to a reliable source, vitamin D is essential for healing wounds since it controls growth factors and other substances that help develop new tissue.
According to a different study, those who have leg ulcers are more likely to be vitamin D deficiency symptoms.
The researchers found that those who consumed 50,000 international units (IU) of vitamin D each week for two months had faster-wound healing.
Who is impacted by a vitamin D deficiency?
Anyone, including infants, toddlers, and adults, can be vitamin D deficiency symptoms.
People who wear clothing that covers a lot of their skin and have darker skin, especially in Middle Eastern nations, may be more likely to suffer from vitamin D deficiency symptoms.
Complications
Rickets
Rickets is an uncommon condition that arises from vitamin D deficiency symptoms.
The illness mostly affects infants and young children in the preschool years, but it can also affect older children.
It can result in the legs bowing and has an impact on how the ribs, wrists, knees, and bones develop.
Vitamin D pills and ensuring that the diet contains enough calcium are two ways that doctors treat rickets.
Cardiovascular disease
According to a reliable source, there is a link between low vitamin D levels and an increased risk of cardiovascular disease.
This may be due to vitamin D’s role in heart health and its ability to reduce inflammation.
An older review discovered that metabolic syndrome and hypertension, two disorders that raise the risk of developing cardiovascular disease, are associated with low vitamin D levels.
Immune disorder
Vitamin D is a natural immune modulator, and researchTrusted Source suggests that low levels of the vitamin may be connected to autoimmune diseases, including:
- type 1 diabetes
- multiple sclerosis
- rheumatoid arthritis
- Crohn’s disease
Who is most at risk for Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms?
A person’s risk of vitamin D deficiency symptoms is enhanced by biological and environmental variables in addition to medical diseases that can cause it. These factors include:
Age: As your skin’s capacity to produce vitamin D declines with time, those over 65 are particularly at risk for developing a vitamin D deficit.
Additionally, infants run the danger of not getting enough vitamin D. Given that breast milk only contains a little quantity of vitamin D, this is especially true for newborns who are exclusively fed it.
Skin color: It’s more difficult for dark-colored skin to make vitamin D from sunlight than light-colored skin, so people with darker skin are at a higher risk for vitamin D deficiency.
Mobility: Sun exposure cannot be used as a source of vitamin D for persons who are housebound or rarely venture outside (such as residents of nursing homes and other facilities). As a result, they are more susceptible to vitamin D insufficiency.
How is vitamin D deficiency treated?
Reaching and then maintaining a sufficient amount of vitamin D deficiency symptoms in your body are the objectives of both treatment and prevention for vitamin D deficiency.
Your doctor would probably advise taking vitamin D pills even if you might think about increasing your intake of foods rich in vitamin D and receiving more sunlight.
There are two types of vitamin D: D2 and D3. Plants provide ergocalciferol, or vitamin D2. Animals provide cholecalciferol or vitamin D3.
To purchase D2, you need a prescription. However, D3 can be purchased over the counter. D3 is easier for your body to absorb than D2.
Consult your doctor to determine whether you require a vitamin supplement and, if so, how much to take.
How can I prevent Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms?
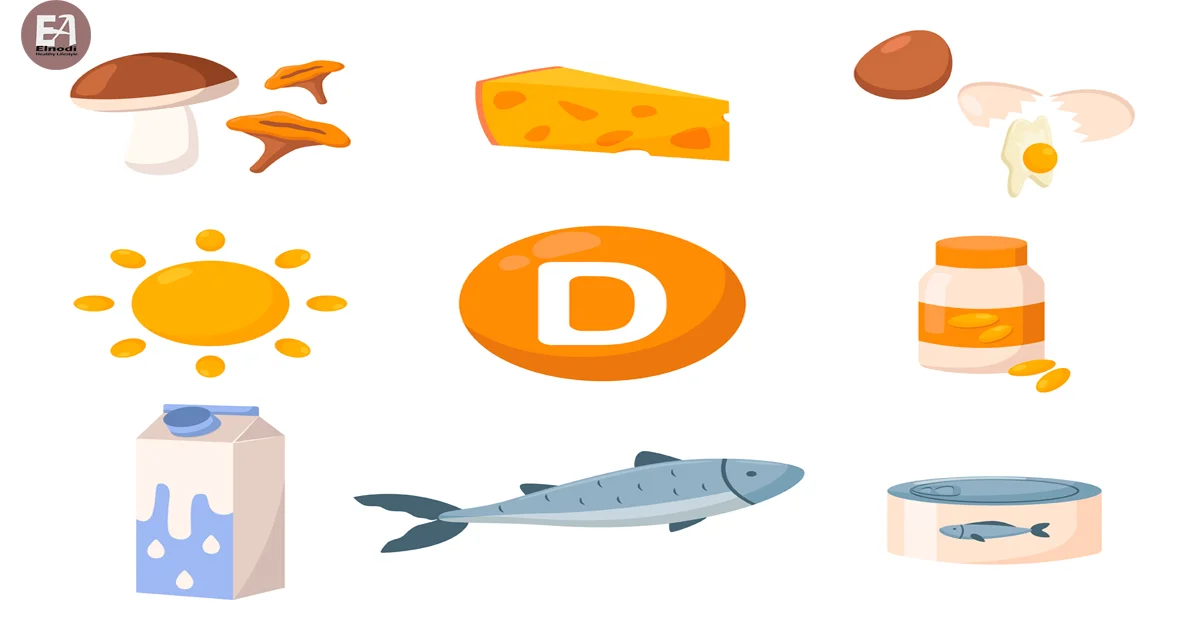

Getting adequate vitamin D from your diet and/or from sun exposure is the best strategy to avoid vitamin D deficiency.
However, avoid spending too much time outdoors without sunscreen. Your chance of developing skin cancer increases if you spend too much time in the sun.
Your age determines how much vitamin D you need daily. Below is a list of the typical daily recommended dosages in micrograms (mcg) and international units (IU).
| Age / Life Stage | Recommended Amount |
| Infants up to 12 months old | 10 mcg (400 IU) |
| People 1 to 70 years old | 15 mcg (600 IU) |
| Adults 71 years and older | 20 mcg (800 IU) |
| Pregnant and breastfeeding people | 15 mcg (600 IU) |
Food sources
| Food source | Portion size | Percentage of the daily value |
| Cod liver oil | 1 tablespoon | 170 |
| Cooked rainbow trout | 3 ounces | 81 |
| Cooked sockeye salmon | 3 ounces | 71 |
| White mushrooms exposed to UV light | 0.5 cup | 46 |
| Fortified 2% milk | 1 cup | 15 |
You can also get vitamin D from fortified foods. Be sure to check the nutrition labels to find out if a food has vitamin D. Foods that often have added vitamin D include:
- Cow’s milk and soy, almond, and oat milk.
- Breakfast cereals.
- Orange juice.
- Other dairy products, such as yogurt.
Summary
People frequently lack vitamin D deficiency symptoms, and they may not even be aware of it.
Anyone exhibiting such symptoms should consult a physician. A healthcare professional should be consulted before using supplements in excess of the daily suggested dose.
Vitamin D deficiency symptoms include fatigue, muscle weakness, bone pain, depression, and even cancer.
Vitamin D helps regulate calcium levels in the body.
Vitamin D is found naturally in foods like fatty fish, eggs, milk, and cheese.
Frequently asked questions
What happens if your vitamin D is low?
Is low vitamin D something to worry about?
What food is highest in vitamin D?
Do bananas have vitamin D?
What is a normal vitamin D level?
In nanograms per milliliter (ng/mL) units, 25-hydroxy vitamin D levels are considered normal. Numerous professionals advise a range of 20 to 40 ng/mL. Some experts advise a range of 30 to 50 ng/mL.