We delve into the detrimental landscape of “Bad Habits for the Brain,” dissecting many compelling reasons why your mind may not be operating at its full potential. Brace yourself for an insightful expedition that goes beyond the ordinary, unraveling the hidden intricacies of habits that could be silently sabotaging your cognitive prowess. Join us as we uncover the secrets, challenge the norms, and empower you with the knowledge to foster a brain-boosting lifestyle. It’s time to bid farewell to the habits that hinder and embrace a future where your brain thrives. Welcome to a realm where awareness transforms into action, and the journey to optimal mental fitness begins.
Bad Habits for the Brain
1. Sleep deprivation damages the brain
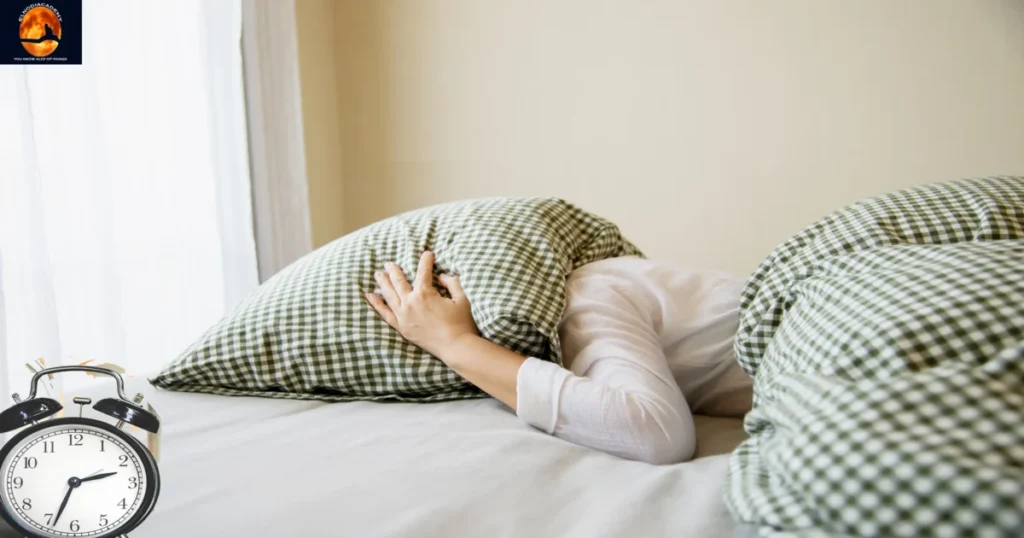

Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of dementia can be brought on by sleep deprivation. As a result, it’s important to get to bed on time. If you don’t get enough sleep, you should refrain from using electronics or consuming alcohol or caffeine right before bed. Instead, establish a calming, peaceful nighttime routine. Be aware that sleeping with your head covered will raise the concentration of CO2 and lower the concentration of O2, both of which can harm your brain.
2. Spending too much time alone
Social interaction is a natural part of being human. The number of Facebook friends you have is not as significant as having a genuine sense of connection. One statistic states that those with even a small circle of close friends are typically happier and more productive than those who live solitary lives. Additionally, they have a lower risk of Alzheimer’s and cognitive deterioration. If you’re feeling lonely, give your friends a call or take up a new socially engaging activity like dancing, badminton, tennis, or social volunteering.
3. Overindulging in snacks
Parts of the brain related to learning, memory, and mental health are smaller in individuals who consume large amounts of burgers, fries, and soft beverages. Desserts high in sugar, in particular, can interfere with the body’s ability to absorb nutrients and protein, leading to malnutrition and perhaps affecting brain development.
Berries, whole grains, nuts, and green leafy vegetables, on the other hand, slow down mental aging and retain brain function. Thus, attempt to replace your usual snack of a bag of chips with a handful of nuts (walnuts, almonds, etc.).
4. The volume on the headphones is too high.
In as little as thirty minutes, you can irreversibly harm your hearing by wearing headphones at maximum volume. Elderly hearing loss is not limited to the ears; it has also been connected to brain issues, including Alzheimer’s disease and brain tissue loss. The brain may have to work too hard to process the voices around it, making it difficult for it to retain what it has heard. Therefore, try not to use the headphones constantly for several hours and reduce the level to no more than 60% of the device’s maximum volume.
5. Poor diet
When, what, and how much you consume are all important to your brain. Have you ever experienced tension headaches after missing a meal? Your brain is telling you to feed it or else it will cease. Try to develop the habit of only eating when you are hungry and never skip a meal. Recall that your diet has a significant role as well.
6. excessive alcohol consumption, smoking, and illicit drug use

Since we’re discussing habits, let’s talk about these criminals who, regrettably, hook too many people and cause unnecessary deaths. Consider that light to moderate drinking poses no issues. This assumption might no longer be supported by research. Light to moderate alcohol use has been linked to a lower risk of dementia and stroke in the past, although the evidence from these studies is regarded as weak and the results have been inconsistent. Right now, it’s safer to presume that consuming less alcohol is ideal.
There’s no advantage to smoking, and most smokers wish to stop. Please visit your doctor for assistance if you smoke or vape and are unable to break your habit. The same applies to illegal drugs. What about cannabis and the brain, though? Cannabis reduces focus, coordination, and attention span. Put simply, it causes cognitive slowness and forgetfulness. Medical marijuana may be helpful for several ailments, such as some childhood epilepsies and nausea during chemotherapy, but the risks of using the drug should be carefully considered against the advantages for each patient.
7. Consuming too much
Even the healthiest foods won’t be enough if you overeat since your brain won’t be able to develop robust neural networks that support memory and thought processes. Furthermore, consuming excessive amounts of food over an extended period might result in obesity, which raises your risk of heart disease, diabetes, and high blood pressure. All have a connection to cognitive issues and Alzheimer’s disease. It’s been proposed that eating too much also hardens the arteries in the brain, which impairs brain function.
8. Staying too long in the dark
Your brain’s activity may slow down if you experience depression due to insufficient natural light. Studies have also demonstrated that exposure to sunlight can help shield the brain from damage.
9. Overindulging in junk food

Overindulging in junk food can be harmful to your brain, just like overeating in general is. Junk food is detrimental to overall health, which includes mental wellness. It may surprise you to hear that persons who eat more fries, potato chips, hamburgers, and soft beverages have smaller brain regions related to mental health, learning, and memory. Junk food is high in calories and sugar, which increases the risk of diabetes and obesity. Furthermore, as we’ve already discussed, these medical issues can harm your brain. Make sure you consume a balanced diet low in junk food if you want to safeguard your brain.
10. Negative Thinking
It is a habit that can harm your brain to think negatively. Your mental health suffers when you’re anxious and stressed all the time. Depression, anxiety, and even dementia may result from this. Studies suggest that those who obsess over negative things have higher levels of tau and amyloid deposits in their brains. One important marker of Alzheimer’s disease is these deposits. Fortunately, it’s not too difficult to break this behavior. To maintain the health of your brain, make sure your ideas are constructive. If you are unable to alter your thought process on your own, visiting a mental health professional could be helpful in some situations.
How to get rid of Bad Habits for the Brain
Embarking on the journey to liberate your mind from the clutches of detrimental habits is a profound commitment to self-improvement. In this exclusive guide, we present a curated roadmap on “How to Get Rid of Bad Habits for the Brain.” The intricacies of the mind demand a nuanced approach, and here, we unfold a personalized strategy tailored to empower you in overcoming cognitive pitfalls.
- Mindful Unraveling: Delve into a self-discovery journey. Identify the habits that impede your cognitive prowess. Awareness is the first step towards transformation.
- Replace and Reinforce: Bid farewell to destructive habits by actively replacing them with positive alternatives. Reinforce the rewiring of your brain through consistent, constructive actions.
- Strategic Detox: Implement a cognitive detox. Purge your mind of negativity and toxic influences. Surround yourself with stimuli that nurture growth and mental well-being.
- Holistic Wellness Integration: Embrace a holistic approach. Integrate brain-boosting habits into your lifestyle, encompassing nutrition, physical activity, and restful sleep for a well-rounded mental fitness regimen.
- Accountability Partnerships: Forge alliances with like-minded individuals. Establish accountability partnerships to support each other on the journey to breaking free from detrimental habits.
- Mindfulness Practices: Cultivate mindfulness. Incorporate meditation, deep breathing, and mindfulness practices to anchor your focus and strengthen your mental resilience against the allure of destructive habits.
- Progress Tracking: Chart your progress meticulously. Regularly assess your advancements, celebrating victories and adjusting strategies as needed. This tracking process solidifies commitment and enhances self-awareness.
- Professional Guidance: Seek professional guidance when needed. Psychologists, therapists, or life coaches can offer valuable insights and strategies to navigate the complexities of breaking free from ingrained habits.
The bottom line
Feels too much? This is because bad habits are notoriously hard to break and there is seldom a one-size-fits-all method for doing so. Repetition is the source of both positive and negative habits. Choose one or two things to start with that you can modify or eliminate. Replace the negative habits with positive ones. Consult your physician for guidance if you are aware that a habit is detrimental to the health of your brain but are finding it difficult to break. The benefits of new batteries, filters, and oil will be felt by your brain machine.